In the world of materials, one term that’s gaining traction is ACM coating. But what exactly is it, and why does it matter? In this article, we break down ACP coating in plain language, exploring what it’s made of, how it works, and why industries are adopting it. Join us as we unravel the basics of ACM coating, providing clear and severe insight into this essential material.
What is an Aluminum Composite Panel (ACP)?
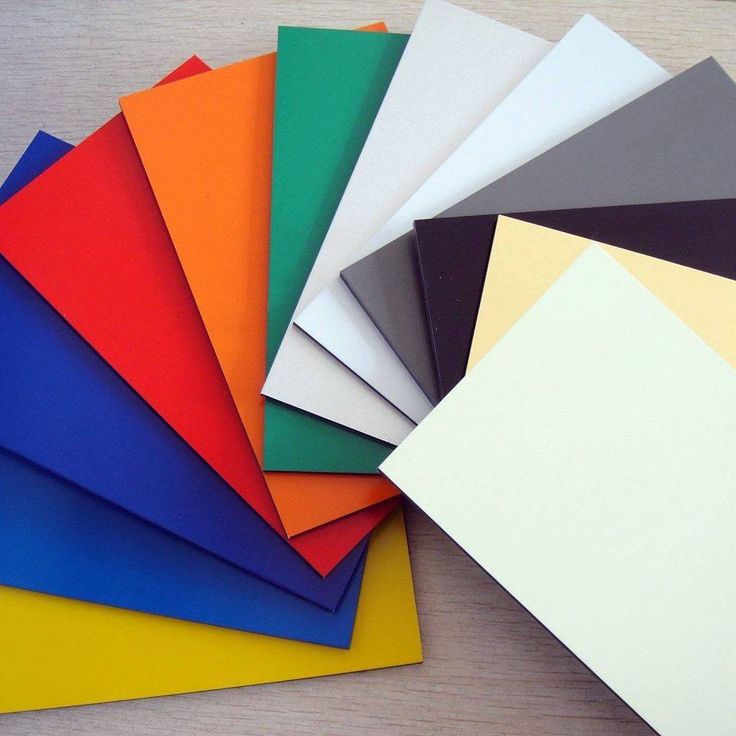

An Aluminum Composite Panel (ACP) is a metal panel with a flat structure, consisting of two slender aluminum sheets adhered to a core material, usually composed of polyethylene (PE) or a mineral-filled substance.
The purpose of combining these materials is to create a lightweight yet sturdy structure suitable for various applications in construction and design.
The outer aluminum layers provide durability, weather resistance, and a sleek finish, while the inner core adds strength and insulation properties. ACPs are commonly used for building facades, signage, interior design, and more due to their versatility and aesthetic appeal.
They come in various colours, finishes, and thicknesses, making them a popular and versatile choice for architects and designers looking for a cost-effective and visually appealing cladding material. Additionally, ACPs are relatively easy to install, making them a practical choice for residential and commercial projects.
What is ACP Coating?

ACP coating refers to applying a protective layer on the surface of an Aluminum Composite Panel (ACP). This coating serves several essential purposes, including enhancing the panel’s durability, weather resistance, and aesthetic appeal. ACP coatings are typically made from various materials, such as polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) or polyester, both of which offer different levels of protection and finishes.
Types of ACM Coatings
- Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Coating: PVDF coatings are known for their exceptional durability and resistance to harsh weather conditions, UV rays, and chemicals. ACPs with PVDF coatings are long-lasting and maintain color and finish even in challenging outdoor environments. These coatings are commonly used in high-end architectural projects where durability and color retention are crucial.
- Polyester Coating: Polyester coatings are more budget-friendly compared to PVDF coatings. While not as resistant to weather and UV exposure as PVDF, polyester-coated ACPs offer decent protection against the elements. They are a popular choice for indoor applications or projects with a lower budget.
Benefits of ACM Panels Coating
ACM (Aluminum Composite Material) coating offers a range of benefits, making it a popular choice in various industries. Here are some critical advantages of ACM coating:
Durability:
ACM coating provides a protective layer that enhances the durability of the material. It shields the underlying structure from environmental factors such as UV rays, moisture, and pollutants, preventing corrosion and maintaining the integrity of the panels over time.
Weather Resistance:
ACM coatings are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, including extreme heat, cold, rain, and wind. This weather resistance ensures that the panels retain their appearance and structural integrity even in challenging outdoor environments.
Color Retention:
The coating materials used in ACM panels, especially PVDF coatings, offer excellent color retention properties. This means the panels retain their original colors for an extended period, reducing the need for frequent repainting or maintenance.
Low Maintenance:
Due to their weather resistance and color retention capabilities, ACM-coated panels require minimal maintenance. Regular cleaning is usually sufficient to keep them looking new, saving time and money for building owners and maintenance teams.
Lightweight:
ACM panels are lightweight, making them easy to handle, transport, and install. Their low weight simplifies the installation process and reduces the structural load on buildings, making them a practical choice for various construction projects.
Versatility:
ACM coatings come in various colors, finishes, and textures, allowing for versatile design options. Architects and designers can choose from various aesthetic elements to create visually appealing facades, signage, and decorative building elements.
Fire Resistance:
Some ACM coatings are designed to be fire-resistant, meeting specific fire safety standards and regulations. Fire-resistant coatings enhance the safety of buildings, making them suitable for commercial and residential applications.
Customization:
ACM coatings can be customized to achieve specific visual effects and textures, allowing for tailored solutions based on project requirements. This customization capability gives architects and designers creative freedom in their designs.
Environmentally Friendly:
Many ACM coatings are eco-friendly, using sustainable materials and manufacturing processes. Additionally, their long lifespan and low maintenance requirements contribute to their environmental sustainability.
Energy Efficiency:
ACM panels can be designed to improve energy efficiency by incorporating insulation materials in the core. This helps regulate indoor temperatures, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling and consequently lowering energy consumption.
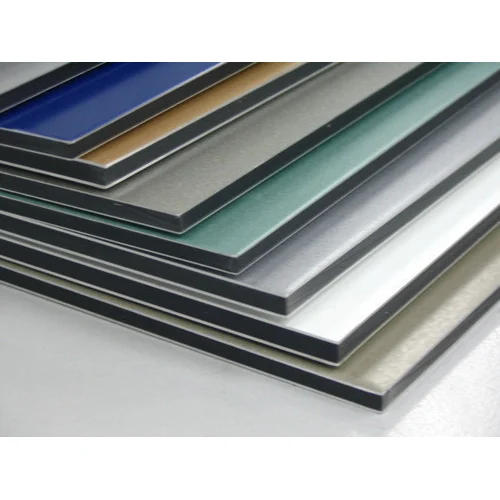
ACP Coating Process
The ACP coating process involves applying a protective layer onto the surface of an Aluminum Composite Panel (ACP) to enhance its durability, weather resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Here’s a simplified overview of the typical ACP coating process:
Surface Preparation:
Before coating, the surface of the aluminum sheets is cleaned and chemically treated to remove impurities, ensuring proper adhesion of the coating material.
Coating Material Preparation:
The coating material, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) or polyester resin, is prepared according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Pigments are added to create the desired color and finish.
Coating Application:
There are several methods for applying the coating onto the aluminum sheets:
Coil Coating:
In this method, the coating material is applied to the aluminum coil before it’s formed into panels. The coated coil is then heated, allowing the coating to bond with the aluminum surface uniformly.
Spray Coating:
Alternatively, the coating material can be applied directly onto the formed ACP panels using a spray gun. This method provides flexibility for customization and touch-ups.
Curing:
After the coating is applied, the ACP panels go through a curing process. Curing involves subjecting the coated panels to controlled heat, which helps the coating material to solidify and bond firmly with the aluminum surface. This step ensures the durability and longevity of the coating.
Quality Control:
Coated ACP panels undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure uniformity, adhesion, color consistency, and resistance to various environmental factors. Quality control measures are in place to identify and rectify defects in the coated panels.


